In the old days, efficiency (doing things right) ruled. You made money by having more efficient processes than competitors, so your margin was higher on the same price. Scale was rewarded, because it brought efficiency, encouraging huge companies and standardised products. Flexibility was your enemy.
Now, technology has changed everything. Just because it is possible, effectiveness (doing the right thing) will rule. The customer will always be right, whatever they want. Can you imagine people now accepting Henry Ford’s statement that people could have any colour they wanted, so long as it was black? Scale and efficiency is not the only thing that matters any more – in this new world, value comes from responsiveness. Success requires using connections, building a community with customers and suppliers, and being creative.
In the days when efficiency led, market domination was the objective, because that was what allowed you to hold onto your “most efficient producer” badge. In the new world, domination is not the only determinant of success. Your company needs to be like a lumberjack on a log flume – constantly moving to stay on top despite the logs rolling, and needing the agility that comes most easily to small companies to do so.
Use consultants and interims for ideas and flexibility
This model lends itself readily to the de-centralised organisation, using consultants, interims, and other forms of flexible working to provide the skills needed when they are needed. To do this well, the organisation needs to be networked and connected; old-style hierarchies, linear processes and so on inhibit the flexibility required. In this post-Brexit-vote world, where no-one quite knows where we are going or what it will mean, that flexibility to adapt rapidly as the shape of the future emerges will be even more important. Winning will depend on having a culture which embraces flexibility and adapts to change. Darwin had a phrase for it: survival of the fittest. The species that survived were the ones with most variability. Work flexibly; bring in and try out new ideas; find better ways to succeed. Voting to be dinosaurs can’t change the laws of nature.
It was only in the latter stages of the referendum campaign that the penny dropped for me. I realised that the reason that the campaign was so much about emotion and so little about facts and likely consequences was that, whatever its ostensible purpose, the referendum had come to be about who we are. My identity is what I believe it to be, and what those I identify with believe it to be. The outcome of a referendum does not, cannot, change that, even if it can lead to a change of status.
It would obviously be nonsense if, when you asked someone whether they would be best off staying married or getting divorced, they stated their gender as the answer. Politicians have allowed a question about relationship to be given an answer about identity. Apples and oranges. In so doing they have shot themselves – and at the same time the whole country – in the foot.
 How do you do that? It is job of the vision you present to make people feel that they want to belong to the new future, and so to accept the discomfort of modifying their sense of identity. If people don’t buy into that vision, your chances of making the change successfully are low.
Whether or not it was deliverable, the ‘Leave’ campaign presented a simple vision of the future based on an identity which was clearly appealing to those disposed to believe it was. If ‘Remain’ presented a vision at all, it certainly did not make much attempt to sell an identity. It is reasonable to ask people about their identity, but we have representative democracy because you will still get the identity answer even if you ask them a relationship question.
If you want to bring about a successful change, start by making sure you have a believable vision which protects peoples’ identity and sense of belonging. Then campaign for that, even if it is not directly what the change is about.
How do you do that? It is job of the vision you present to make people feel that they want to belong to the new future, and so to accept the discomfort of modifying their sense of identity. If people don’t buy into that vision, your chances of making the change successfully are low.
Whether or not it was deliverable, the ‘Leave’ campaign presented a simple vision of the future based on an identity which was clearly appealing to those disposed to believe it was. If ‘Remain’ presented a vision at all, it certainly did not make much attempt to sell an identity. It is reasonable to ask people about their identity, but we have representative democracy because you will still get the identity answer even if you ask them a relationship question.
If you want to bring about a successful change, start by making sure you have a believable vision which protects peoples’ identity and sense of belonging. Then campaign for that, even if it is not directly what the change is about.
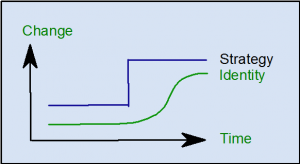
Identity and change
There is a profound lesson about change there. Identity is perhaps the ‘stickiest’ phenomenon in culture, because belonging is so fundamental to our sense of security. A change project is often perceived as changing in some way the identity of that to which we belong. However, peoples’ sense of identity changes much more slowly than the strategy. If we do not take steps to bridge the identity gap while people catch up, it is the relationship which is in for trouble. How do you do that? It is job of the vision you present to make people feel that they want to belong to the new future, and so to accept the discomfort of modifying their sense of identity. If people don’t buy into that vision, your chances of making the change successfully are low.
Whether or not it was deliverable, the ‘Leave’ campaign presented a simple vision of the future based on an identity which was clearly appealing to those disposed to believe it was. If ‘Remain’ presented a vision at all, it certainly did not make much attempt to sell an identity. It is reasonable to ask people about their identity, but we have representative democracy because you will still get the identity answer even if you ask them a relationship question.
If you want to bring about a successful change, start by making sure you have a believable vision which protects peoples’ identity and sense of belonging. Then campaign for that, even if it is not directly what the change is about.
How do you do that? It is job of the vision you present to make people feel that they want to belong to the new future, and so to accept the discomfort of modifying their sense of identity. If people don’t buy into that vision, your chances of making the change successfully are low.
Whether or not it was deliverable, the ‘Leave’ campaign presented a simple vision of the future based on an identity which was clearly appealing to those disposed to believe it was. If ‘Remain’ presented a vision at all, it certainly did not make much attempt to sell an identity. It is reasonable to ask people about their identity, but we have representative democracy because you will still get the identity answer even if you ask them a relationship question.
If you want to bring about a successful change, start by making sure you have a believable vision which protects peoples’ identity and sense of belonging. Then campaign for that, even if it is not directly what the change is about.  Have you ever noticed that the fruit and nuts in your breakfast muesli tend to stay at the top of the packet? So that when you are getting toward the end of the packet, you are usually left with mostly the boring bits?
There is a simple explanation. When there are many large lumps (the fruit and nuts) together, they have large holes in between them, and smaller lumps (the oats) can fall through the holes. When many small lumps are together, they have small holes in between them, so large lumps can’t fall through. Consequently, with gentle shaking there is a tendency for the large and small lumps to separate, with the large lumps at the top.
Interesting, but so what? Well, perhaps the same sort of thing happens with the order of work activities. The interesting, strategic lumps stay at the top and get done first. The boring – or difficult – bits may fall through the cracks, or at least get left to others or to later. The trouble is that to have a nutritionally balanced diet, we need the whole mixture, not just the exciting bits. Good delivery requires us to stick to doing things in the best order, even when that means tackling early some activities we would rather leave till later.
Have you ever noticed that the fruit and nuts in your breakfast muesli tend to stay at the top of the packet? So that when you are getting toward the end of the packet, you are usually left with mostly the boring bits?
There is a simple explanation. When there are many large lumps (the fruit and nuts) together, they have large holes in between them, and smaller lumps (the oats) can fall through the holes. When many small lumps are together, they have small holes in between them, so large lumps can’t fall through. Consequently, with gentle shaking there is a tendency for the large and small lumps to separate, with the large lumps at the top.
Interesting, but so what? Well, perhaps the same sort of thing happens with the order of work activities. The interesting, strategic lumps stay at the top and get done first. The boring – or difficult – bits may fall through the cracks, or at least get left to others or to later. The trouble is that to have a nutritionally balanced diet, we need the whole mixture, not just the exciting bits. Good delivery requires us to stick to doing things in the best order, even when that means tackling early some activities we would rather leave till later.
Yesterday I spent the morning at WBMS, in a fascinating workshop run by Quirk Solutions exploring the value of ‘Wargaming’ as a way of testing the resilience of a strategy and related plans before putting them into effect.
Wargaming, as you might imagine, is based on the process developed by the military to evaluate their plans, but that is where any direct connection to anything military ends. If you called the process something else, nothing about it would tell you its origins. And in practice, it is really a somewhat more formalised and disciplined extension of testing approaches which you may well already use to some extent. Where Chis Paton and his team at Quirk really add value is in their in-depth experience of what works, and highly-polished skills for facilitating the process to make it maximally effective.
I took away a number of key ideas for running a good process which I thought it would be worth sharing.
Wargaming
The process is based around two teams: the Blue (plan-owning) Team and the Red (plan-challenging) Team. Although that sounds similar to the common approach of ‘Red Team Review’ for proposal improvement, in this process it is made more effective by asking each Red Team player to represent the views of a major interested party or parties. This makes for a much more engaged and lively process, better bringing out emotive issues. It can also bring out the important potential conflicts between different interests which may otherwise be ‘averaged out’. At least some of the Red Team can be externals – where there are no commercial issues, they could even be the relevant interest groups themselves! – which is clearly likely to help avoid blind spots. Even in a brief exercise, it was clear that the role-playing approach could bring much greater richness to the output. The process is also iterative: the Blue Team present their outline plan (best not to develop too much detail early, as it is likely to change!); the Red Team make challenges back from their ‘interest’ perspectives; the Blue Team re-work the proposal to address as many of the issues as possible; further challenge, and so on. Clearly in a relatively brief review meeting, there will be very limited time for further analysis or data gathering between iterations, so the objective is not a finished plan, but the best possible framework to take away and work up, together with lists of actions and owners. That leads me to my final point: While a Red Team Review would normally be looking at a more-or-less finished proposal, the process we tested will add most value early in the process of development. No-one likes to make significant changes to a plan that they have put a lot of effort into, however important, and that may well lead to the smallest adaptation possible, rather than the best. Thanks WBMS and Quirk for organising a stimulating event!
So, seven articles later, where does that leave us? We have talked about 15 principles for designing your internal governance, and I have listed them all together for you below for convenience. However, I do want to re-emphasise one thing I said at the beginning:
“What good governance is NOT about is bureaucracy, box-ticking and delays. It requires finding balances – between control and practical delivery; between the risks of delegation and the cost of control; between wide ownership of decisions and strong accountability for them; between a simple structure and efficient decision-making; between minimum overhead and an effective audit trail – which provide the optimum basis for success. Every organisation has different arrangements because the optimum trade-offs depend on the context.”
The principles for internal governance are just the things you should have in mind when you design your system. That does not mean that the result has to be complicated. It should be ONLY as complicated as you need it to be in your particular circumstances. If you are a large public sector organisation, it may be necessary to be at the high-control end of the spectrum. If you are a small development company, you probably need something much lighter-weight and more flexible – but that is not a reason for not thinking about it. Some principles are good-practice rules which are likely to apply everywhere. Others are choices you need to make. The important thing is that the choices you make should be deliberate, and should be consistent. By deciding exactly what principles for internal governance you are going to work to before you start, you give yourself the best chance of success.
15 Principles for Internal Governance
- Authority and accountability must go together.
- No-one will have authority to ‘mark their own homework’ (i.e. conflicts of interest will be avoided).
- Collective and Individual Authority are different. What will their respective roles and interfaces be in the structure you will create?
- The governance structure should be strictly hierarchical. All bodies which have Collective Authority must have a place within that hierarchy.
- Individual Authority is delegated through the line management arrangements, but it forms part of the overall governance structure and must join up seamlessly with the rest of it.
- The design should start by establishing those areas where the Board should make delegations (starting by noting the matters already reserved to the Board), and how they should be grouped.
- What (if any) dual-key approval arrangements are desirable?
- The authority grid should include qualitative as well as quantitative delegation limits, and should not be restricted to areas where a financial limit can be set.
- Escalation levels will be set to provide an appropriate volume of requirements to escalate, decided on the basis of business need and practical delivery.
- Decisions about committee membership should be made in the light of the delegation levels set, not the other way round.
- The list of staff (or roles) to be included as members of the Collective Authority bodies will balance the need for ownership of decisions with minimum meeting membership.
- Clear rules for meeting attendance will be agreed and maintained.
- What formal documentation (e.g. Terms of Reference, Letters of Appointment) will be mandated?
- In what circumstances will formal authorisation and/or acceptance of documentation be mandated?
- How widely will the arrangements be communicated?
- The Midas Touch - what is Governance for?
- The Midas Touch again - Starting to build Internal Governance
- The Midas Touch again - Authority and Accountability in Internal Governance
- How many ways can you design a tree? - Hierarchy in Internal Governance
- Snakes and Ladders - Delegation and Escalation in Internal Governance
- Why are YOU here? Choosing members of Internal Governance Meetings
- What's in a word? Documentation for Governance
 Do you know where you are trying to get to? Are you sure? Could you write down clearly and succinctly what the output will be, or what success would look like? Are your objectives SMART (or at least clear)?
Often people fight shy of being that specific. The trouble is, when you are, success or failure become black and white. And that raises the stakes.
Or it may be that they just find it too hard to write such a specification – and it is hard. It forces you think through options and to make choices, often on inadequate information, and that requires a lot of confidence.
Leaving things a bit vague is more comfortable on both counts, but also makes it much less likely that you will deliver what you really wanted to. That is partly because you have less motivation to do so, but it is also partly because clarity helps everyone in the team to see the contribution they need to make. If the overall objectives are not clear, different people will interpret them differently, and their contributions will not necessarily all be exactly what is needed. It also provides a poor example for them to follow – it means that each of their contributions is also more likely to have a vague specification, and so may deviate even further from requirements.
Setting clear objectives is the first essential of leadership: if you don’t know exactly where you want to go, how can you lead other people on the journey? As the song goes, “If you don’t know where you’re going, any road’ll take you there”.
Do you know where you are trying to get to? Are you sure? Could you write down clearly and succinctly what the output will be, or what success would look like? Are your objectives SMART (or at least clear)?
Often people fight shy of being that specific. The trouble is, when you are, success or failure become black and white. And that raises the stakes.
Or it may be that they just find it too hard to write such a specification – and it is hard. It forces you think through options and to make choices, often on inadequate information, and that requires a lot of confidence.
Leaving things a bit vague is more comfortable on both counts, but also makes it much less likely that you will deliver what you really wanted to. That is partly because you have less motivation to do so, but it is also partly because clarity helps everyone in the team to see the contribution they need to make. If the overall objectives are not clear, different people will interpret them differently, and their contributions will not necessarily all be exactly what is needed. It also provides a poor example for them to follow – it means that each of their contributions is also more likely to have a vague specification, and so may deviate even further from requirements.
Setting clear objectives is the first essential of leadership: if you don’t know exactly where you want to go, how can you lead other people on the journey? As the song goes, “If you don’t know where you’re going, any road’ll take you there”.
[caption id="" align="alignright" width="300"] Tyrannosaurus rex, Palais de la Découverte, Paris (Photo credit: Wikipedia)[/caption]
Evolution is the natural process by which all forms of life adapt to changes in their environment. It is a very slow process, in which many small changes gradually accumulate. It is unplanned and undirected: who knows how the environment may change in the future, and so what adaptations would put us ahead of the game? Successful changes are not necessarily the best possible choices, merely the best of those that were tested. Different individuals start from different places, and so the adaptations which seem to work will vary. Consequently, over time, divergence will occur until different species result, even though each species can be traced back to a common ancestor. But evolution is brutal too: not all species will make it. Some find they have gone down an evolutionary dead end, and some that change is simply too fast for them to adapt to.
Sometimes organisational change can be like this. I once worked for a public-sector organisation which was privatised, so that it had to change from being ‘mission-led’ to being profit-led. Management set out a vision for what it wanted the organisation to become – essentially a similar, unitary, organisation but in the private sector – but was unable to make the radical changes necessary to deliver it fast enough. Evolution carried on regardless as the primary need to survive forced short-term decisions which deviated from the vision. Without a unifying mission as a common guide, different parts of the organisation evolved in different ways to adapt to their own local environments. Fragmentation followed, with a variety of different destinies for the parts, and a few divisions falling by the wayside. Despite starting down their preferred route of unitary privatisation, the eventual destination was exactly what the original managers had been determined to avoid.
What is the lesson? Ideally of course it should be possible to set out a strategic objective, and then to deliver the changes needed to get there. But if the change required is too great, or the barriers mean change is brought about too slowly, the short-term decisions of evolution may shape the future without regard to management intentions. That does not necessarily make the outcome worse in the greater scheme of things: after all, evolution is about survival of the fittest. But natural selection is an overwhelming force, and if short-term decisions are threatening to de-rail management’s strategic plan, it may be wise to take another look at the plan, and to try to work with evolution rather than against it.
Tyrannosaurus rex, Palais de la Découverte, Paris (Photo credit: Wikipedia)[/caption]
Evolution is the natural process by which all forms of life adapt to changes in their environment. It is a very slow process, in which many small changes gradually accumulate. It is unplanned and undirected: who knows how the environment may change in the future, and so what adaptations would put us ahead of the game? Successful changes are not necessarily the best possible choices, merely the best of those that were tested. Different individuals start from different places, and so the adaptations which seem to work will vary. Consequently, over time, divergence will occur until different species result, even though each species can be traced back to a common ancestor. But evolution is brutal too: not all species will make it. Some find they have gone down an evolutionary dead end, and some that change is simply too fast for them to adapt to.
Sometimes organisational change can be like this. I once worked for a public-sector organisation which was privatised, so that it had to change from being ‘mission-led’ to being profit-led. Management set out a vision for what it wanted the organisation to become – essentially a similar, unitary, organisation but in the private sector – but was unable to make the radical changes necessary to deliver it fast enough. Evolution carried on regardless as the primary need to survive forced short-term decisions which deviated from the vision. Without a unifying mission as a common guide, different parts of the organisation evolved in different ways to adapt to their own local environments. Fragmentation followed, with a variety of different destinies for the parts, and a few divisions falling by the wayside. Despite starting down their preferred route of unitary privatisation, the eventual destination was exactly what the original managers had been determined to avoid.
What is the lesson? Ideally of course it should be possible to set out a strategic objective, and then to deliver the changes needed to get there. But if the change required is too great, or the barriers mean change is brought about too slowly, the short-term decisions of evolution may shape the future without regard to management intentions. That does not necessarily make the outcome worse in the greater scheme of things: after all, evolution is about survival of the fittest. But natural selection is an overwhelming force, and if short-term decisions are threatening to de-rail management’s strategic plan, it may be wise to take another look at the plan, and to try to work with evolution rather than against it.
 Tyrannosaurus rex, Palais de la Découverte, Paris (Photo credit: Wikipedia)[/caption]
Evolution is the natural process by which all forms of life adapt to changes in their environment. It is a very slow process, in which many small changes gradually accumulate. It is unplanned and undirected: who knows how the environment may change in the future, and so what adaptations would put us ahead of the game? Successful changes are not necessarily the best possible choices, merely the best of those that were tested. Different individuals start from different places, and so the adaptations which seem to work will vary. Consequently, over time, divergence will occur until different species result, even though each species can be traced back to a common ancestor. But evolution is brutal too: not all species will make it. Some find they have gone down an evolutionary dead end, and some that change is simply too fast for them to adapt to.
Sometimes organisational change can be like this. I once worked for a public-sector organisation which was privatised, so that it had to change from being ‘mission-led’ to being profit-led. Management set out a vision for what it wanted the organisation to become – essentially a similar, unitary, organisation but in the private sector – but was unable to make the radical changes necessary to deliver it fast enough. Evolution carried on regardless as the primary need to survive forced short-term decisions which deviated from the vision. Without a unifying mission as a common guide, different parts of the organisation evolved in different ways to adapt to their own local environments. Fragmentation followed, with a variety of different destinies for the parts, and a few divisions falling by the wayside. Despite starting down their preferred route of unitary privatisation, the eventual destination was exactly what the original managers had been determined to avoid.
What is the lesson? Ideally of course it should be possible to set out a strategic objective, and then to deliver the changes needed to get there. But if the change required is too great, or the barriers mean change is brought about too slowly, the short-term decisions of evolution may shape the future without regard to management intentions. That does not necessarily make the outcome worse in the greater scheme of things: after all, evolution is about survival of the fittest. But natural selection is an overwhelming force, and if short-term decisions are threatening to de-rail management’s strategic plan, it may be wise to take another look at the plan, and to try to work with evolution rather than against it.
Tyrannosaurus rex, Palais de la Découverte, Paris (Photo credit: Wikipedia)[/caption]
Evolution is the natural process by which all forms of life adapt to changes in their environment. It is a very slow process, in which many small changes gradually accumulate. It is unplanned and undirected: who knows how the environment may change in the future, and so what adaptations would put us ahead of the game? Successful changes are not necessarily the best possible choices, merely the best of those that were tested. Different individuals start from different places, and so the adaptations which seem to work will vary. Consequently, over time, divergence will occur until different species result, even though each species can be traced back to a common ancestor. But evolution is brutal too: not all species will make it. Some find they have gone down an evolutionary dead end, and some that change is simply too fast for them to adapt to.
Sometimes organisational change can be like this. I once worked for a public-sector organisation which was privatised, so that it had to change from being ‘mission-led’ to being profit-led. Management set out a vision for what it wanted the organisation to become – essentially a similar, unitary, organisation but in the private sector – but was unable to make the radical changes necessary to deliver it fast enough. Evolution carried on regardless as the primary need to survive forced short-term decisions which deviated from the vision. Without a unifying mission as a common guide, different parts of the organisation evolved in different ways to adapt to their own local environments. Fragmentation followed, with a variety of different destinies for the parts, and a few divisions falling by the wayside. Despite starting down their preferred route of unitary privatisation, the eventual destination was exactly what the original managers had been determined to avoid.
What is the lesson? Ideally of course it should be possible to set out a strategic objective, and then to deliver the changes needed to get there. But if the change required is too great, or the barriers mean change is brought about too slowly, the short-term decisions of evolution may shape the future without regard to management intentions. That does not necessarily make the outcome worse in the greater scheme of things: after all, evolution is about survival of the fittest. But natural selection is an overwhelming force, and if short-term decisions are threatening to de-rail management’s strategic plan, it may be wise to take another look at the plan, and to try to work with evolution rather than against it.  I’m on my way to a Board meeting. My job as a Board member is to turn up about once a month for a meeting lasting normally no more than a couple of hours to take the most important decisions the company needs – decisions which are often about complex areas, fraught with operational, commercial, legal and possibly political implications, and often with ambitious managers or other vested interests arguing strongly (but not necessarily objectively) for their preferred outcome. Few of the decisions are black and white, but most carry significant risk for the organisation. Good outcomes rely on informing Board members effectively.
This is a well-managed organisation, so I have received the papers for the meeting a week in advance, but I have had no chance to seek clarification of anything which is unclear, or to ask for further information. In many organisations, the papers may arrive late, or they may have been poorly written so that the story they tell is incomplete or hard to understand (despite often being very detailed), or both. The Board meeting, with a packed agenda and a timetable to keep to, is my only chance to fill the gaps.
I have years of experience to draw on, but experience can only take me so far. Will I miss an assumption that ought to be challenged, or a risk arising from something I am not familiar with? If that happens, we may make a poor decision, and I will share the responsibility. In some cases – for instance a safety issue - that might have serious consequences for other people. It’s not a happy thought.
I’m on my way to a Board meeting. My job as a Board member is to turn up about once a month for a meeting lasting normally no more than a couple of hours to take the most important decisions the company needs – decisions which are often about complex areas, fraught with operational, commercial, legal and possibly political implications, and often with ambitious managers or other vested interests arguing strongly (but not necessarily objectively) for their preferred outcome. Few of the decisions are black and white, but most carry significant risk for the organisation. Good outcomes rely on informing Board members effectively.
This is a well-managed organisation, so I have received the papers for the meeting a week in advance, but I have had no chance to seek clarification of anything which is unclear, or to ask for further information. In many organisations, the papers may arrive late, or they may have been poorly written so that the story they tell is incomplete or hard to understand (despite often being very detailed), or both. The Board meeting, with a packed agenda and a timetable to keep to, is my only chance to fill the gaps.
I have years of experience to draw on, but experience can only take me so far. Will I miss an assumption that ought to be challenged, or a risk arising from something I am not familiar with? If that happens, we may make a poor decision, and I will share the responsibility. In some cases – for instance a safety issue - that might have serious consequences for other people. It’s not a happy thought.



